The Role of Genetic Mutations in Alzheimer's Disease: Understanding the Mechanisms
- Posted on May 18, 2023
- Lifestyle
- By ojashwini shrivastava
- 779 Views

Alzeimer's disease:-
Introduction to Alzeimer's disease:
Alzheimer's disease is a progressive neurological disorder that primarily affects memory, thinking, and behavior. It is the most common cause of dementia, a general term for a decline in cognitive abilities. While the exact cause of Alzheimer's remains unknown, researchers have discovered that mutations in Certain genes play a significant role in the development of this debilitating condition.
What is Alzheimer's disease?
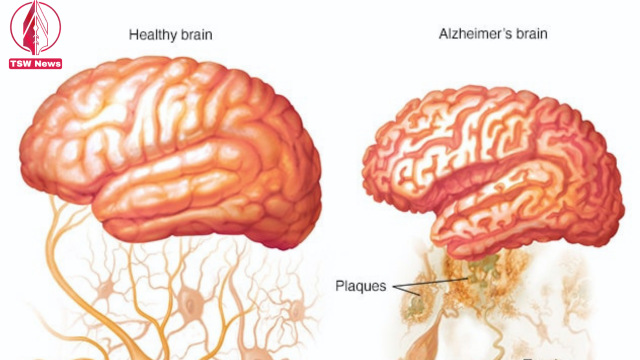
Alzheimer's disease is a chronic and irreversible brain disorder that affects millions of people worldwide. It is characterized by the formation of plaques and tangles in the brain, which disrupt the normal functioning of nerve cells. Over time, these abnormalities spread and cause a decline in cognitive abilities, eventually leading to memory loss, confusion, and difficulties in performing daily tasks.
How is Alzheimer's disease caused?
The precise causes of Alzheimer's disease are not yet fully understood, but researchers have identified several risk factors that contribute to its development. One significant factor is genetic mutations. Mutations in specific genes, such as the amyloid precursor protein (APP) and presenilin 1 and 2 (PSEN1 and PSEN2), have been found to be associated with familial or early-onset Alzheimer's disease. These mutations affect the processing of proteins in the brain, leading to the accumulation of amyloid plaques and tau tangles, which are characteristic features of the disease.
What are the Symptoms of Alzheimer's Disease?
The symptoms of Alzheimer's disease vary from person to person but generally progress over time. Initially, individuals may experience mild memory loss and difficulties with language or problem-solving. As the disease advances, they may face challenges in completing familiar tasks, become disoriented in time and space, exhibit changes in mood or behavior, and eventually lose the ability to recognize loved ones. These symptoms can significantly impact the individual's quality of life and their ability to function independently.
How can you Diagnose Alzheimer's Disease?
Diagnosing Alzheimer's disease is complex and typically involves a comprehensive evaluation by healthcare professionals. Medical history, neurological exams, cognitive tests, and brain imaging techniques are used to assess memory, thinking, and behavior. Additionally, genetic testing may be conducted to identify specific mutations that could contribute to the development of the disease, especially in cases of early-onset Alzheimer's.
What are the Cures for Alzheimer's Disease?
Currently, there is no cure for Alzheimer's disease. Treatment options primarily focus on managing symptoms and slowing down the progression of the disease. Medications may be prescribed to enhance memory and cognitive functions, alleviate behavioral and psychological symptoms, or regulate neurotransmitters in the brain. Additionally, non-drug approaches such as cognitive stimulation, occupational therapy, and support from caregivers can help improve the individual's quality of life.
How Can We Prevent Alzheimer's Disease?
While there is no guaranteed way to prevent Alzheimer's disease, adopting a healthy lifestyle can potentially reduce the risk. Regular exercise, a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids, maintaining social engagement, and challenging the brain through activities like puzzles or learning new skills have been associated with a lower risk of developing Alzheimer's. Managing chronic conditions like hypertension, diabetes, and obesity may also contribute to reducing the risk.
Conclusion:
Alzheimer's disease is a devastating condition that impacts millions of individuals worldwide. Although the exact cause is not fully understood, genetic mutations play a significant role in its development. Understanding the genetic factors associated with Alzheimer's can lead to better diagnostic tools, potential targeted therapies, and improved care for those affected. While there is currently no cure, ongoing research and a focus on prevention offer hope for the Future in tackling this challenging disease and improving the lives of individuals and families impacted by Alzheimer's.
For more updates keep visiting our website www.topstoriesworld.com where we provide unbiased, true and top stories of the world.


